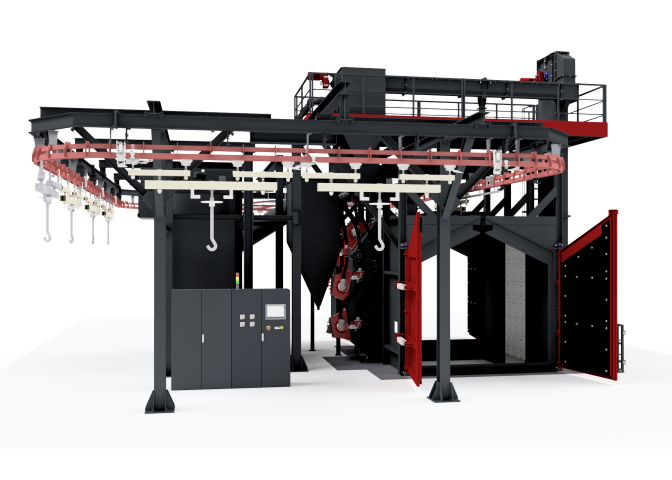
Foundries play a critical role in our daily lives, though most people don’t realize the extent of their impact. From the construction industry to automotive manufacturing, foundries are involved in producing the metals that form the backbone of numerous products we use every day. Despite their ubiquitous presence, many are unaware of the complex processes that occur behind the scenes in these facilities.
Foundries are integral to industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, providing the essential metal components that keep these sectors running smoothly.
Transitioning from the basic definition, let’s dive deeper into the core operations and equipment that drive these metal-making facilities.
What Does a Foundry Do?
Foundries are more than just metal shops. They are places where raw materials are transformed into valuable components through complex processes, contributing to nearly every aspect of industrial life.
A foundry’s role is to melt and mold metals to create castings, which are essential in many industries. Whether it's a car engine, a bridge beam, or an aircraft turbine, foundries are the places where these vital components take shape.
A foundry’s job is to take raw materials—typically metal alloys—and transform them into usable parts. This process is not only vital for industries that rely on metal components but is also fundamental to the broader industrial landscape. Foundries generally follow several crucial steps to ensure high-quality castings: Patternmaking, Molding, Melting, Pouring, Ejection & Cleaning, Fettling, and Inspection.
Each step plays a significant role in ensuring the final product meets precise specifications. For instance, patternmaking involves creating models for the mold, which must be accurate to prevent defects in the final casting. Similarly, melting requires the careful heating of metals to precise temperatures to ensure they can be poured into molds without impurities or irregularities. The pouring process itself is delicate and demands close attention to temperature control to avoid mishaps like metal leakage or uneven casting.
What is the Process Behind Foundry Work?
Understanding the step-by-step flow of a foundry’s operations reveals how complex and meticulous the process is, ensuring that every casting meets industry standards.

The foundry process involves multiple stages that begin with patternmaking and end with inspection, with each stage designed to ensure high-quality results. From shaping molds to cleaning and inspecting castings, the process ensures precision and durability.
In a typical foundry, metal is melted in large furnaces, such as induction or electric arc furnaces, and poured into molds that shape the final product. The importance of material selection for molds cannot be overstated—different materials, like silica sand or resin, have unique properties that make them suitable for specific types of metals or casting techniques. Once the mold is filled with molten metal, it is cooled and solidified before being carefully ejected from the mold.
Post-casting processes are just as important as the initial mold creation. The ejection and cleaning steps ensure that any excess metal is removed, and the casting is free from imperfections. Fettling follows, where excess material is shaved off to give the casting its final form. Finally, each casting undergoes rigorous inspection to confirm that it meets the required dimensions and quality standards.
What Equipment is Used in Foundries?
Foundries rely on specialized equipment to handle the extreme conditions and precision needed during the metalworking process. These machines are integral in ensuring that foundries can consistently produce high-quality castings at scale.
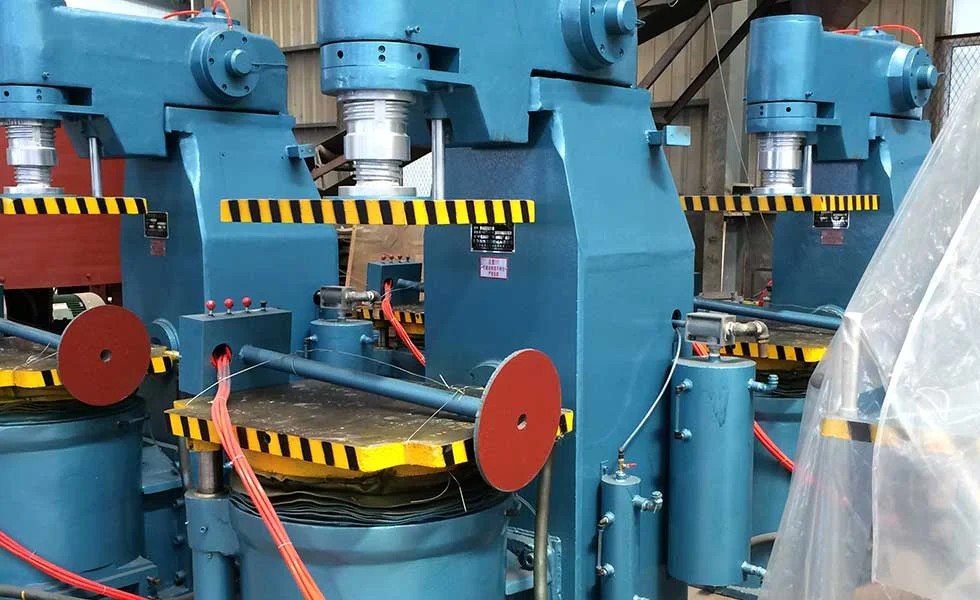
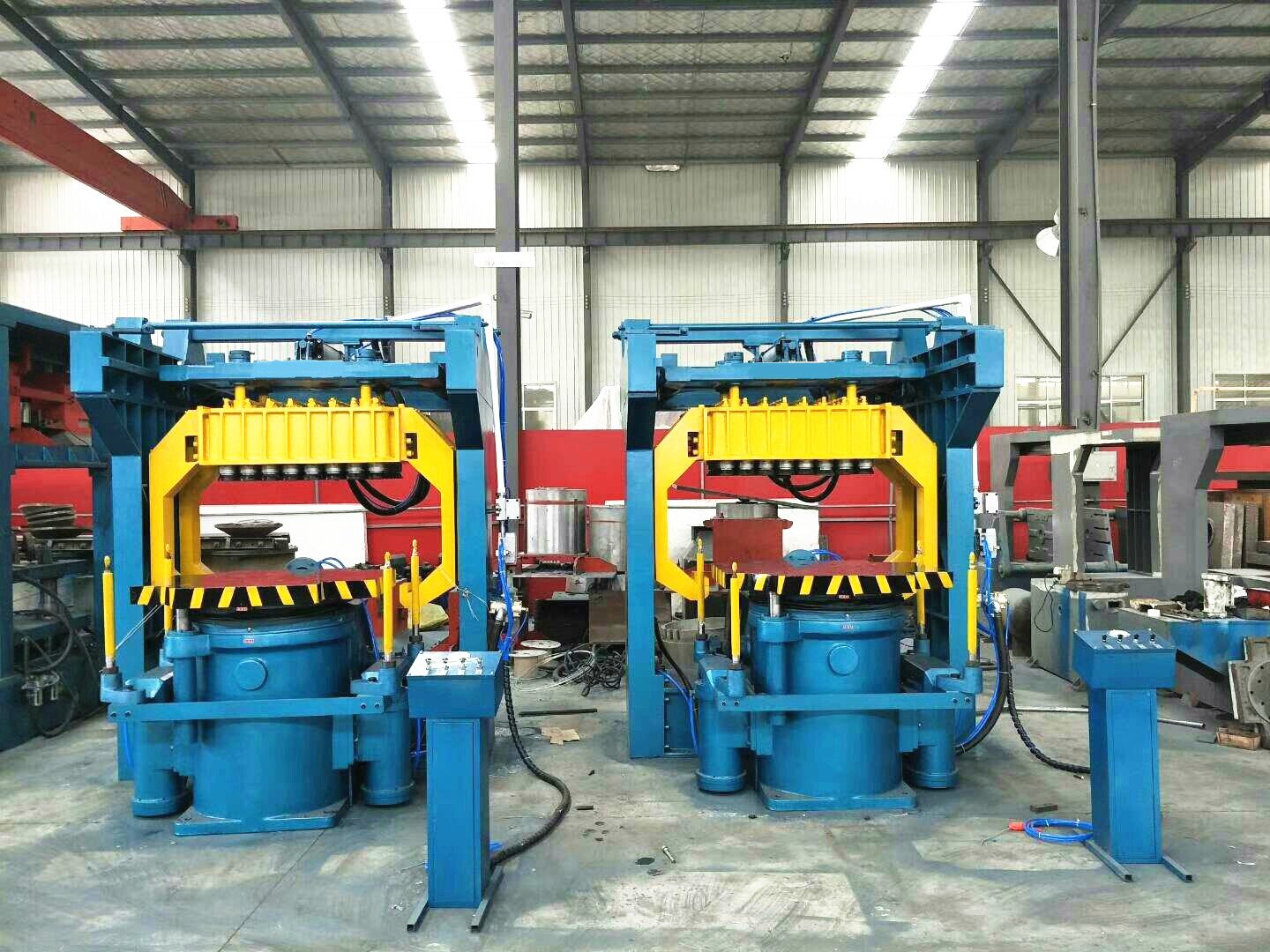
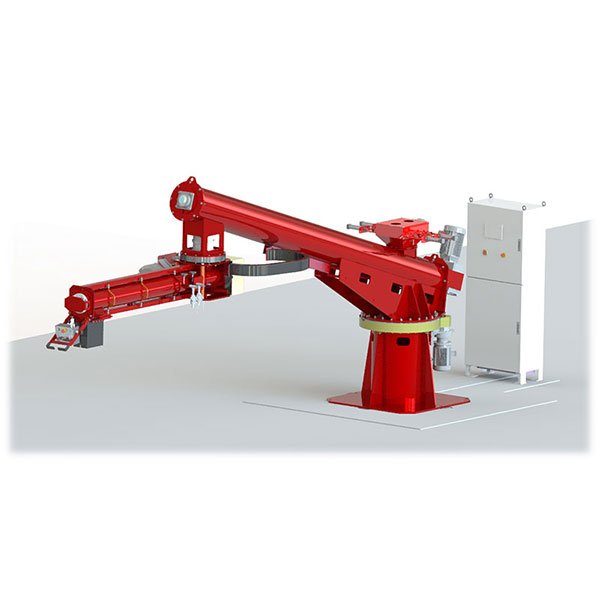
Core equipment in foundries includes furnaces, molds, cranes, and conveyors. Each piece of equipment is designed to withstand the intense heat and mechanical stress involved in metal casting while ensuring efficiency and safety.
Foundries utilize a wide range of equipment designed for the specific tasks required in the casting process. Furnaces, such as electric arc or induction furnaces, are used to melt metals to their molten state. These furnaces are capable of reaching extremely high temperatures and are crucial for processing metals like steel, copper, and aluminum.
Molding machines create the molds that give castings their shape. Molds can be made from various materials, such as sand, metal, or ceramic, depending on the type of casting required. Some foundries may use automated molding machines, while others rely on manual molding processes to ensure precision.
Cranes and lifting equipment are used for handling heavy molds and molten metal. The molten metal must be carefully transported to the molds, where it is poured to create the final product. Conveyors help in the efficient movement of molds and castings throughout the foundry, streamlining the production process.
What Safety Measures Are Taken in Foundries?
Safety in foundries is a top priority, as the environment can be dangerous due to extreme temperatures, heavy machinery, and the presence of molten metals.
Foundries implement stringent safety measures to protect workers, including personal protective equipment (PPE), fire suppression systems, and facility design to reduce risk factors.
The safety of foundry workers is paramount, as they are exposed to hazardous conditions such as extreme heat, steam explosions, and molten metal leaks. One of the most essential aspects of safety in a foundry is the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Workers are required to wear heavy-duty fire-resistant clothing, gloves, face shields, and safety glasses to protect themselves from burns and splashes of molten metal.
Fire suppression systems are also crucial in foundries due to the flammability of some materials. Specialized extinguishing agents, like dry sand or industrial fire extinguishers, are used to control potential fires. Ventilation is another important aspect of foundry design, with high ceilings and powerful ventilation systems to help remove heat and fumes from the facility.
Foundries also focus on the layout of the facility, ensuring that molten metal and workers don’t cross paths unnecessarily. Proper process flow management and well-defined movement paths for workers reduce the chances of accidents, and controls are in place to prevent metal leaks or spills.
How is the Foundry Industry Evolving?
With technological advancements, the foundry industry is adapting to new challenges, such as labor cost reduction, improved automation, and environmental concerns.

Automation, advanced furnace technologies, and sustainability measures are shaping the future of foundries. These innovations are increasing production efficiency, lowering costs, and reducing the environmental impact of metal casting.
The foundry industry has undergone significant changes in recent years, largely driven by automation and the need for greater efficiency. Automated systems are now capable of performing tasks that were once labor-intensive, such as molding and pouring metal. This not only reduces labor costs but also enhances the consistency and quality of the castings produced.
Additionally, modern furnaces are becoming more energy-efficient, helping foundries reduce their environmental footprint. For example, electric arc furnaces are widely used in steel production and are known for their efficiency and reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnaces. In response to environmental concerns, many foundries are adopting recycling processes to minimize waste and reduce the consumption of raw materials.
The future of the foundry industry also lies in adopting green technologies that focus on reducing emissions and energy consumption, while still maintaining high production rates and quality standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foundries are crucial to the industrial world, providing the essential metal components that keep modern economies running. With advances in technology and safety, the foundry industry continues to evolve to meet the growing demands of various sectors while ensuring the well-being of its workers and minimizing environmental impact. As we move forward, the role of foundries in shaping the future of manufacturing and industrial development will remain ever important.