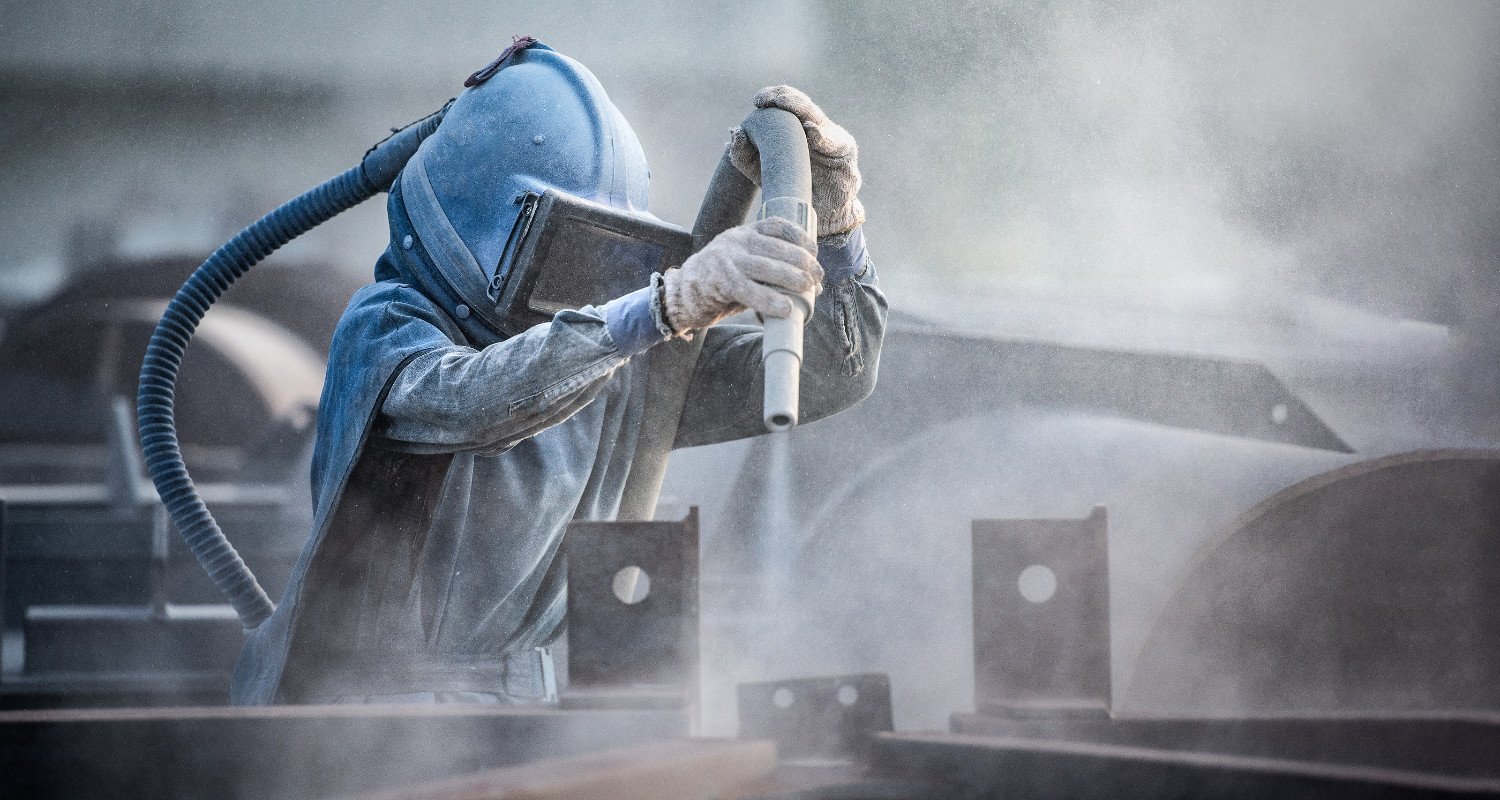
In many industrial sectors, surface treatment plays a crucial role in enhancing the durability and finish of materials. Grit blasting, a common form of surface preparation, is widely used but often misunderstood. So, what does a grit blaster do, and why is it essential for various industries?
A grit blaster is a machine used to clean or prepare the surface of a material by propelling abrasive particles (grit) at high speeds. This process removes contaminants, rust, old paint, or imperfections, creating a smooth and even surface that is ready for coating, painting, or further processing.
The purpose of grit blasting is to enhance material properties, such as increasing paint adhesion or preparing surfaces for welding. But how does it work, and how does it differ from other similar processes?
How does a grit blaster work?

The grit blasting process involves propelling small abrasive particles (grit) at high velocity onto the surface of a workpiece. This is usually achieved by pressurized air or a centrifugal system. The grit particles hit the material's surface, causing it to roughen or clean it, depending on the application.
Grit blasting machines typically consist of three main components:
- Blasting Machine: This is where the grit or abrasive material is stored and fed into the blasting system.
- Compressor or Centrifugal Wheel: The source of energy that propels the abrasive particles. Air pressure is the most common method, although centrifugal wheels can be used for more consistent and faster results.
- Blast Hose and Nozzle: These direct the abrasive material onto the surface of the workpiece. The operator holds the hose or uses an automated system for specific areas.
How It Works:
- Step 1: The abrasive grit is loaded into the machine and fed into the blasting system.
- Step 2: Pressurized air or a rotating wheel propels the grit towards the surface of the workpiece.Pressurized Air in Blasting
- Step 3: As the grit strikes the surface, it removes contaminants, rust, old coatings, and debris. It also roughens the surface, which can improve adhesion for coatings or enhance the material’s finish.
The power and consistency of the blasting process depend on factors like air pressure, grit type, nozzle size, and distance from the workpiece.
Key Benefits of Grit Blasting:
- Effective Cleaning: Removes stubborn contaminants like rust, old paint, and scale.
- Surface Preparation: Roughens surfaces to improve coating adhesion.
- Versatility: Works on a variety of materials like metals, concrete, and stone.
What is the difference between grit and shot blasting?
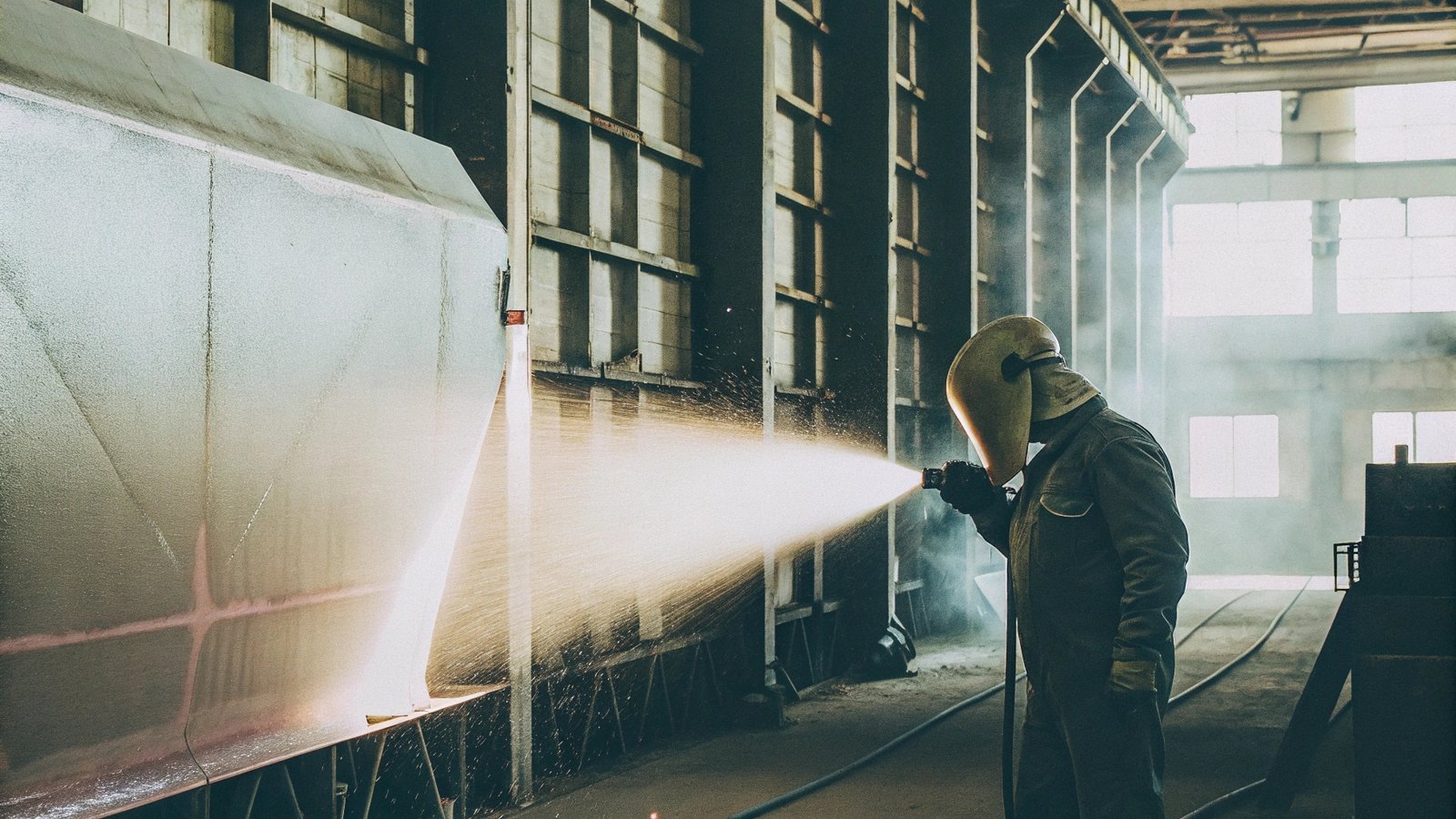

While both grit blasting and shot blasting are used for surface treatment, they differ in the materials used and the final result achieved. Here's how the two compare:
| Feature | Grit Blasting | Shot Blasting |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Material | Uses angular grit (sand, aluminum oxide, etc.) | Uses round metallic shots (steel, cast iron) |
| Impact Type | Produces a rougher surface due to angular grit | Provides a smoother, more polished finish |
| Application | Cleaning, surface roughening for coatings | Peening, cleaning, deburring |
| Machine Type | Often uses compressed air | Uses a centrifugal wheel to throw shots |
Key Differences:
Grit Blasting: The use of angular abrasives, like sand or aluminum oxide, creates a rougher surface texture. This is ideal when the goal is to prepare a surface for coatings or welding. Grit blasting is often used for removing rust, paint, or old coatings from materials.Grit Blasting Explained
Shot Blasting: In contrast, shot blasting uses round metallic shots, which are propelled at the surface by centrifugal force. This process is used for cleaning, polishing, or improving the material’s durability through a technique called shot peening.Shot Blasting vs Grit Blasting
While both processes share similar functions, the abrasive materials and impact methods result in different surface finishes.
What is the purpose of grit blasting?

Grit blasting serves several key purposes across various industries. Understanding its primary applications helps companies determine when and why they should incorporate this process into their operations.
Key Purposes of Grit Blasting:
Surface Cleaning: One of the most common uses of grit blasting is cleaning surfaces by removing contaminants like rust, scale, dirt, and old paint. This is especially important in industries where cleanliness is critical for further processing, such as in aerospace or automotive manufacturing.
Improving Adhesion: Grit blasting is often used to roughen a surface, making it more suitable for subsequent coating or painting. This helps to ensure that coatings adhere properly and last longer. For instance, before painting metal surfaces or applying coatings, grit blasting creates the perfect textured surface.
Weld Preparation: When preparing metal surfaces for welding, grit blasting removes any surface oxides and contamination, allowing for better welding results. Clean, roughened surfaces ensure strong weld bonds.
Surface Peening: In some cases, grit blasting is used to enhance the material's fatigue resistance by introducing compressive stress on the surface. This technique, known as shot peening, is particularly important in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Deburring: Grit blasting can also be used for deburring, which involves removing small burrs or sharp edges from a workpiece. This is essential for ensuring smooth surfaces that don’t pose any risk during handling or assembly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grit blasting is an essential surface treatment process that serves multiple purposes, from cleaning and roughening surfaces to preparing them for coatings and welding. Understanding how a grit blaster works, the difference between grit and shot blasting, and the key applications of grit blasting will help industries optimize their production processes and achieve higher quality results.