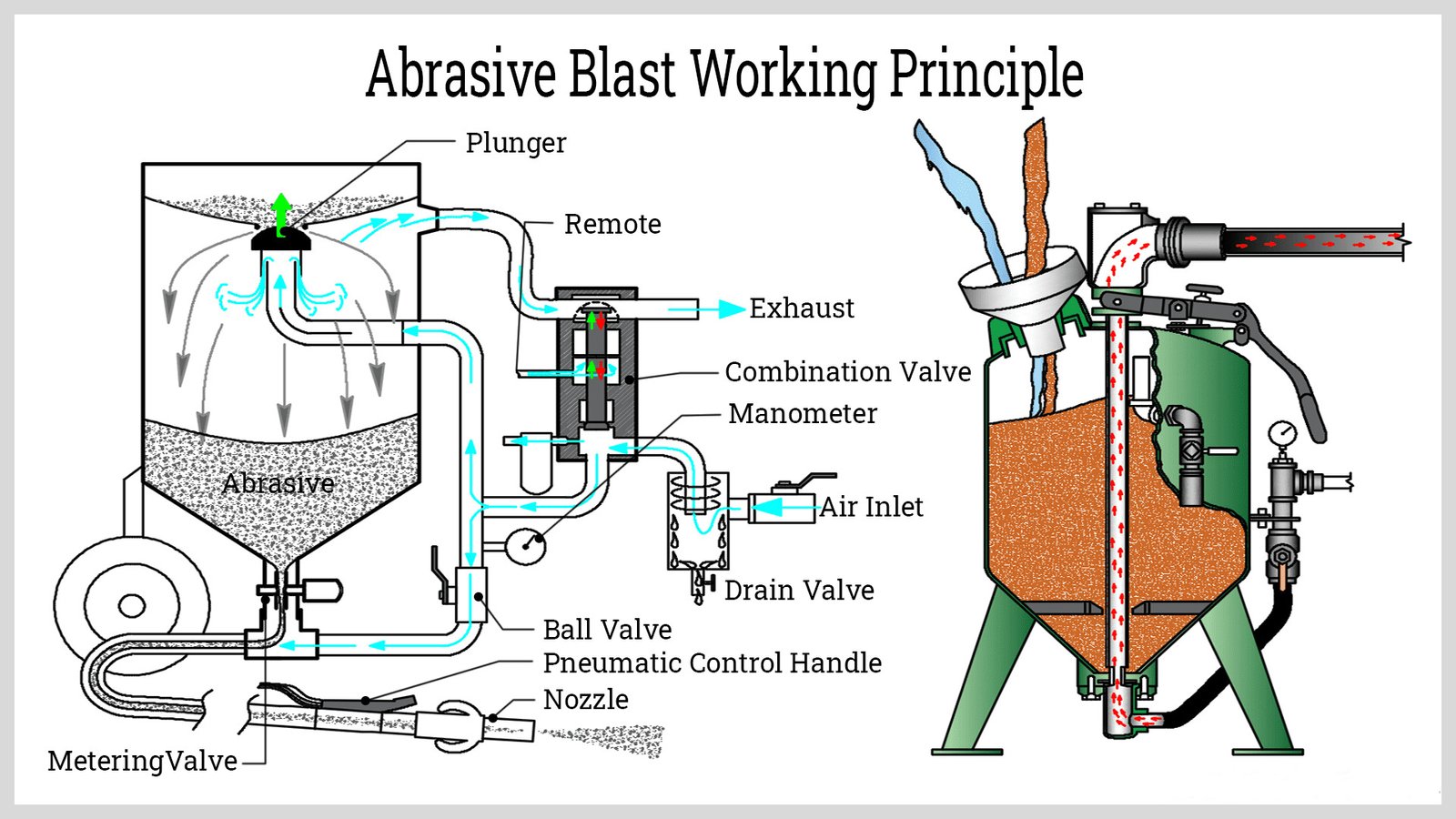
Grit blasting is a transformative surface preparation technique, critical in many industries for cleaning, roughening, or texturizing surfaces efficiently. But how does it work, and why is it so widely used?
Grit blasting is a surface preparation method where high-velocity abrasive particles are propelled to clean, roughen, or texture a surface. It enhances adhesion, removes impurities, and prepares surfaces for coating or bonding in industrial applications.
To truly understand its value, let's delve deeper into the principles, benefits, and nuances of grit blasting.
How does a grit blaster work?
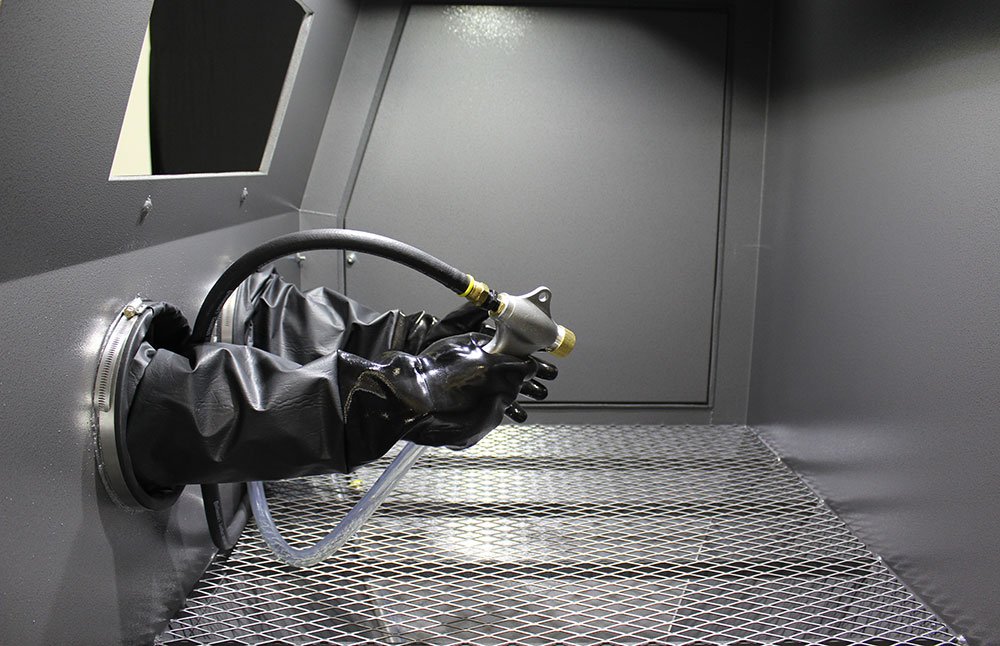

The grit blasting process involves precision and power, transforming surfaces for various industrial needs. But what makes it tick?
A grit blaster works by accelerating abrasive materials through a nozzle using compressed air or high-pressure systems. The abrasive particles impact the surface, removing contaminants and creating desired textures.
Dive Deeper: Mechanics and Key Parameters
The grit blasting process operates in several stages:
- Abrasive Selection: Materials like aluminum oxide or walnut shells are chosen based on substrate properties.
- Pressure Regulation: Typical operational pressures range from 80–100 psi, adjusted for the material's hardness.
- Nozzle Orientation: The angle and distance of the nozzle determine the precision of the treatment.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Abrasive Type | Aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, etc. |
| Particle Size | Larger for rough surfaces, smaller for fine finishes |
| Pressure | 80–100 psi |
| Surface Profile | 2.5–6.5 µm, measured with profilometers |
These controlled dynamics ensure efficient cleaning, enhanced adhesion, and consistent outcomes across various applications.
What is the purpose of grit blasting?
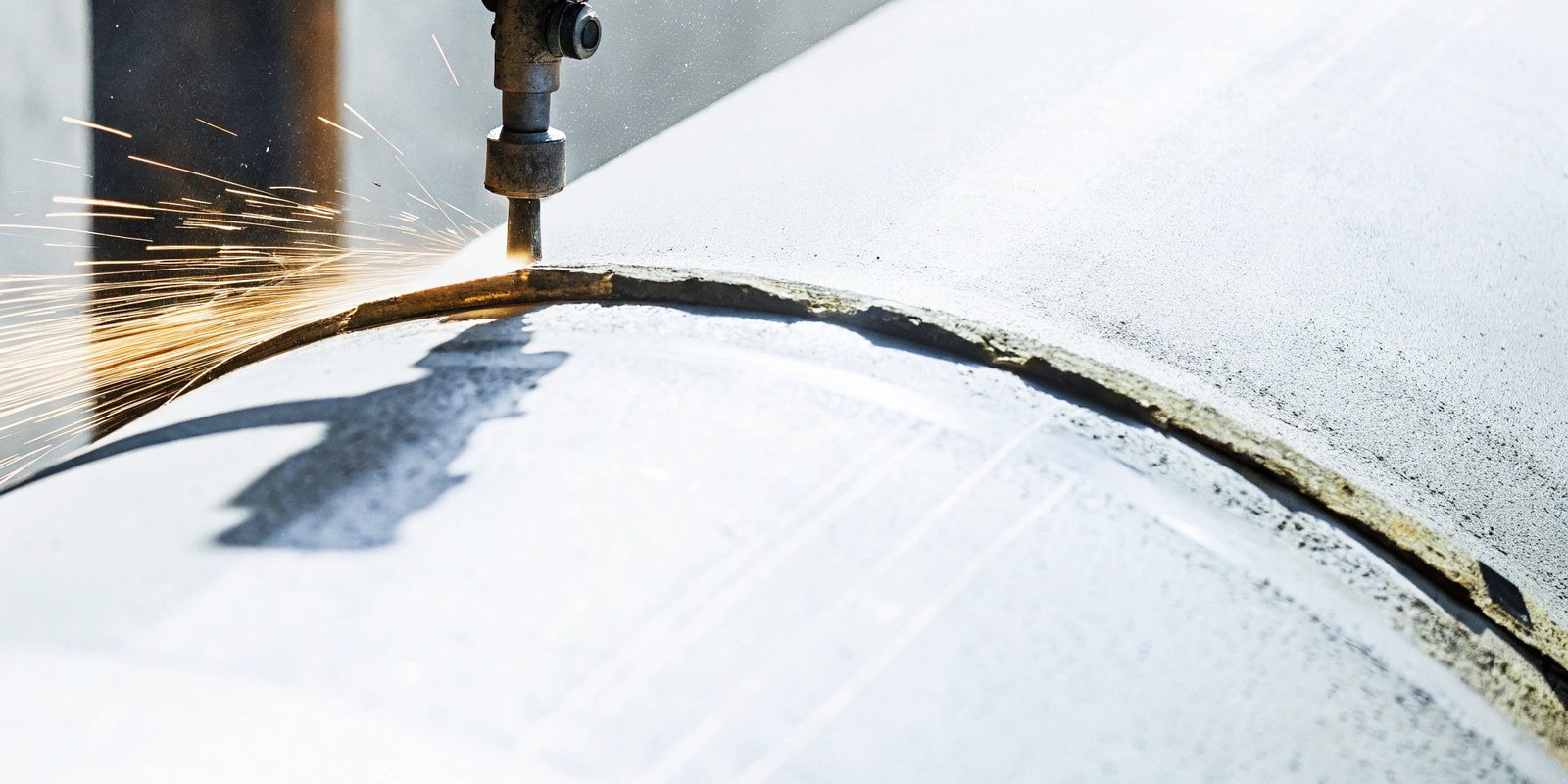

Why is grit blasting such a go-to method for surface preparation?
Grit blasting cleans, roughens, and prepares surfaces, ensuring better adhesion for coatings, paints, or adhesives. It also removes contaminants like rust, old paint, and scale efficiently.
Dive Deeper: Applications and Benefits
Industries leverage grit blasting for its versatility and efficiency:
- Industrial Surface Preparation: Prepares metals like steel and aluminum for protective coatings or paint.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Cleans parts like turbine blades and enhances bonding in composite materials.
- Construction and Maintenance: Restores corroded infrastructure like bridges or pipelines.
| Purpose | Example Applications |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Removes rust, old coatings, and contaminants |
| Texture Creation | Enhances bonding for adhesives and paints |
| Surface Uniformity | Prepares surfaces for high-precision coatings |
By using the right abrasive materials and adjusting pressure settings, grit blasting achieves optimal surface readiness.
What pressure is needed for grit blasting?
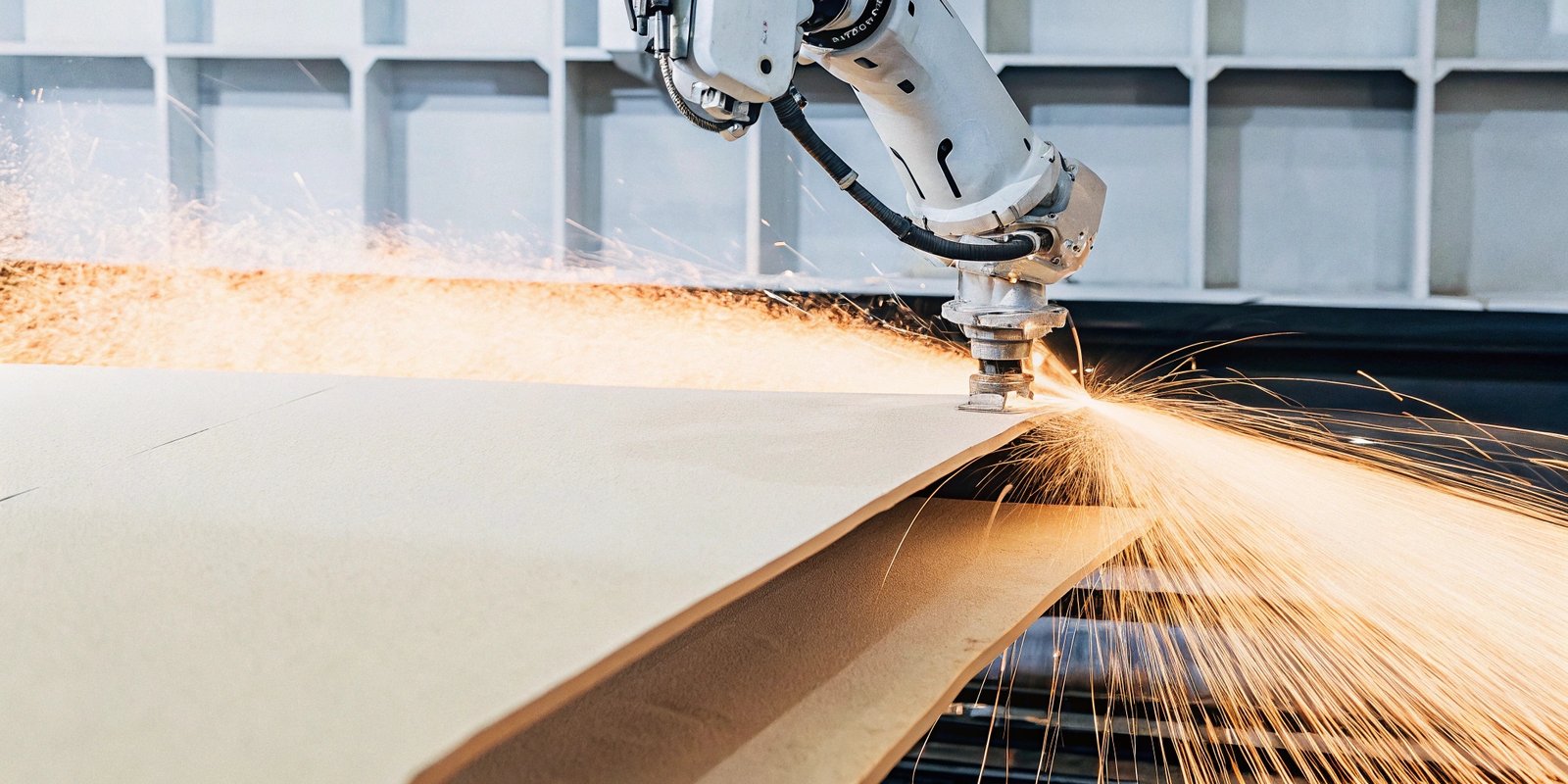

A critical factor in grit blasting is the pressure applied. What’s the right balance for optimal results?
Grit blasting typically requires pressures of 80–100 psi, adjusted according to the substrate material and desired surface finish.
Dive Deeper: Pressure Calibration
Correct pressure ensures effective cleaning without damaging the substrate. Here’s how pressure affects the process:
- Low Pressure (40–60 psi): Suitable for delicate surfaces like plastics or soft metals.
- Medium Pressure (80–100 psi): Ideal for general industrial applications involving steel or aluminum.
- High Pressure (100+ psi): Reserved for robust surfaces or heavy-duty cleaning tasks.
| Material | Recommended Pressure |
|---|---|
| Soft Metals (Aluminum) | 60–80 psi |
| Steel | 80–100 psi |
| Concrete | 100+ psi |
Maintaining the right pressure avoids over-abrasion and ensures consistent surface profiles, making it a vital parameter in grit blasting operations.
What is the difference between sand blasting and grit blasting?
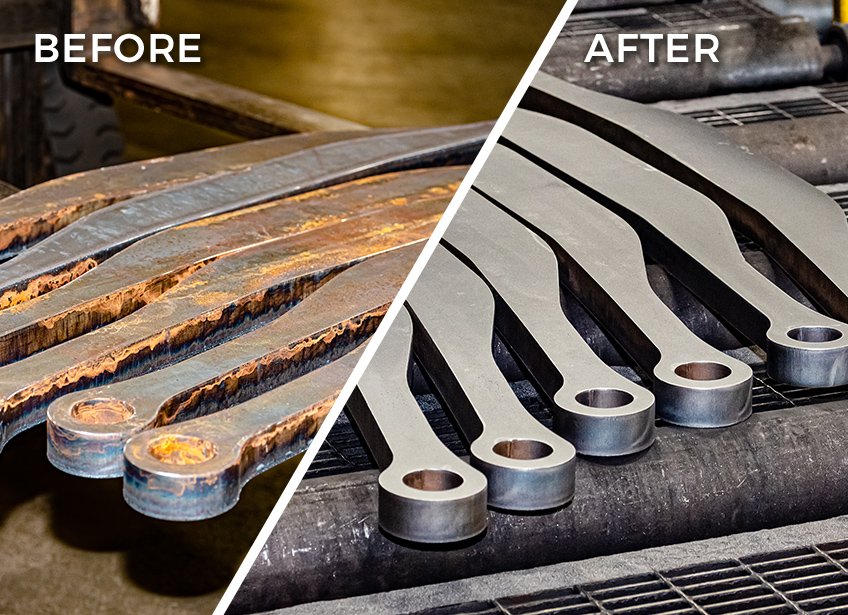

While sandblasting and grit blasting are often used interchangeably, they are distinct methods. What sets them apart?
The key difference is the abrasive material: sandblasting uses silica sand, while grit blasting employs a variety of abrasive particles, offering more versatility and safety.
Dive Deeper: Method Comparison
| Aspect | Sandblasting | Grit Blasting |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Material | Silica sand | Aluminum oxide, steel grit, plastic beads |
| Health Concerns | High risk of silicosis | Safer alternatives available |
| Applications | Limited to basic cleaning | Wide range, including texturing and bonding |
Sandblasting's reliance on silica sand presents health risks, including silicosis, leading to a shift toward safer, more versatile grit blasting techniques.
Conclusion
Grit blasting is a cornerstone of industrial surface preparation, offering unmatched versatility and efficiency. By understanding its mechanics, purposes, and key distinctions, industries can optimize their processes for better adhesion, durability, and surface cleanliness. From automotive to construction, grit blasting remains an indispensable tool in modern engineering.
Whether you’rerefining metal for painting for painting or preparing delicate components for bonding, grit blasting provides the precision and power to meet industrial demands.